“Brainstorming is the nexus of ideas.” – Asa Don Brown, Interpersonal Skills in the Workplace, Finding Solutions that Work
Brainstorming, developed in the early 1940s by advertising executive Alex Osborn, became a tool with staying power.
For companies that provide professional PowerPoint services, it’s important for there to be a collaboration between the client and the company, as the client’s input is vital to how the design experts will approach the project.
Conducting a brainstorming session of your own? Remember that for it to work and not feel like a total waste of time, everybody must be open and respectful to everyone’s ideas and opinions. Problems arise when there are people that think they need to filter good ideas from the bad because of the fear of judgment.
How does it work? In a nutshell, brainstorming consists of three steps:
- Pose a problem or opportunity.
- Ask the team to pitch their ideas, no matter how unusual these may seem—there is no right or wrong idea.
- Review and select the most interesting ideas and then discuss how these can be implemented.
For example, working with marketing presentation consultants require brainstorming so they can translate your specifications and their design into an effective and engaging PowerPoint. If you’re having difficulties in generating ideas on the top of your head, then why not try one of these interesting techniques instead?
Mind Mapping
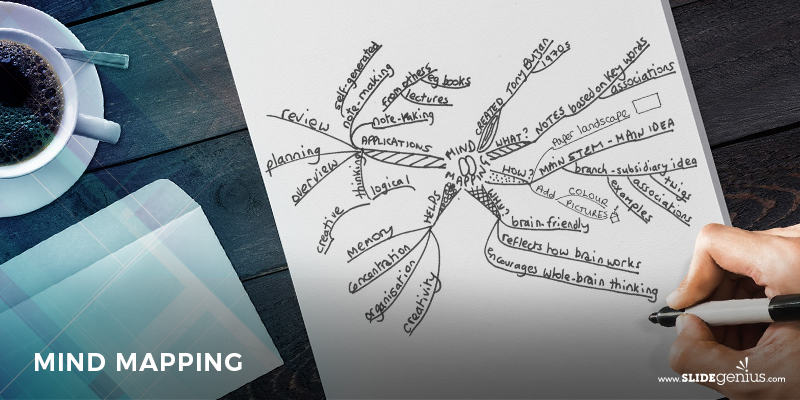
Conceptualized by Tony Buzan in the 1960s, this visual tool enhances the brainstorming process. This organizes thoughts by showing how these can be connected, encouraging the continuous flow of ideas and associations.
SWOT Analysis

This stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats and what this type of brainstorming does is that it helps flesh out ideas in an objective manner. It specifies the goals of the project or business venture, identifying the internal and external factors that may affect its success or failure in the long run.
Starbursting

Usually, people brainstorm to find answers—with starbursting, it focuses on forming questions. It starts with a star, which has product, service, or concept to be discussed, and expands as more questions are asked. The should answer who, what, when, where, why, and how.
Brain-Netting

This involves brainstorming on the Internet, which means team members will share their ideas over a private channel and then discuss it in person. They may also choose to generate and discuss concepts online.
Round Robin
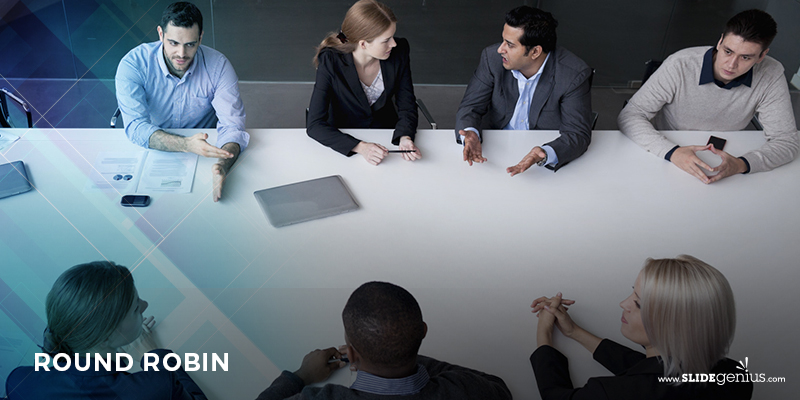

This method of brainstorming gives everybody in the group an opportunity to speak their minds. Once gathered in a circle, members of the group are encouraged to pitch in and contribute, as there are times that one or two people in the group may be too shy to voice their opinion on the subject. Plus, this is a way to keep dominant personalities from taking over the session.
Once everyone has shared their ideas, this is the only time that other members may suggest a second concept.
Brainstorming combines lateral thinking with an informal approach to problem solving. It promotes collaboration among teammates, encouraging each person to be as creative and original as they can. With this tool, it helps companies generate radical solutions to problems.
References:
Tucker, Robert. “Seven Brainstorming Techniques for Your Next Ideation Session.” Forbes. November 16, 2017. https://www.forbes.com/sites/robertbtucker/2017/11/16/seven-brainstorming-techniques-for-your-next-ideation-session/#18a15bb66d5d
“Brainstorming and Mind Mapping.” Monash University. https://www.monash.edu/rlo/research-writing-assignments/understanding-the-assignment/brainstorming#Mindmapping
Madsen, Dag Øivind. “SWOT Analysis: A Management Fashion Perspective.” International Journal of Business Research. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Dag_Madsen/publication/299278178_SWOT_Analysis_A_Management_Fashion_Perspective/links/56f05fee08ae70bdd6c94a74/SWOT-Analysis-A-Management-Fashion-Perspective.pdf







